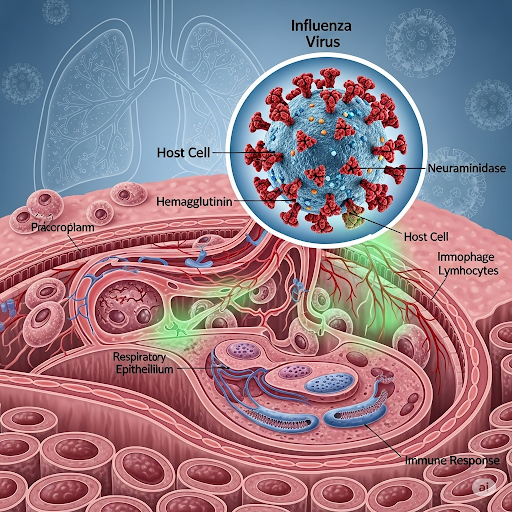
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses. Unlike the common cold, the flu strikes suddenly and can lead to severe complications if not addressed promptly. It primarily affects the nose, throat, and lungs, spreading quickly through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or even talks.
While many people recover within a week or two, influenza can be life-threatening for vulnerable groups such as young children, older adults, pregnant women, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
In this guide, we’ll explore the causes, stages, types, symptoms, treatment options, prevention tips, dietary advice for recovery, risk factors, and the global impact of influenza.
Causes of Influenza
Influenza is primarily caused by infection with influenza viruses. These viruses are classified into four types: A, B, C, and D, each with distinct characteristics and risks.
The virus spreads in multiple ways:
- Airborne droplets: When an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, the virus can travel through tiny droplets in the air.
- Contact with contaminated surfaces: Touching objects such as doorknobs or smartphones that carry the virus and then touching your nose, mouth, or eyes can lead to infection.
- Weak immunity: People with poor nutrition, chronic illnesses, or lack of sleep are more susceptible to influenza.
Good hygiene, a strong immune system, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals are key preventive measures.
Stages of Influenza
Understanding the stages of influenza helps in managing the illness effectively. The progression typically follows these phases:
- Incubation (1–4 days): The virus enters the body, but symptoms have not yet appeared.
- Early Symptoms (Day 1–3): Fever, sore throat, mild cough, and body aches begin.
- Peak Stage (Day 3–5): Symptoms intensify; fatigue and severe cough become more noticeable.
- Recovery Stage (Day 5–7 or longer): Symptoms gradually ease, though weakness and residual cough may persist for several days.
Early recognition and care during these stages can prevent complications and accelerate recovery.
Types of Influenza Viruses
Influenza viruses are divided into four main types:
- Influenza A: Often causes severe illness and can trigger pandemics, such as H1N1.
- Influenza B: Typically responsible for seasonal flu outbreaks; generally less severe than A.
- Influenza C: Causes mild respiratory symptoms and is relatively uncommon.
- Influenza D: Rarely affects humans; primarily infects animals such as cattle.
Knowing the type of influenza can guide treatment strategies and preventive measures.
Symptoms of Influenza
Influenza symptoms appear suddenly and can range from mild to severe. Common signs include:
- High fever and chills
- Sore throat and persistent cough
- Stuffy or runny nose
- Headache and muscle aches
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (more common in children)
Unlike a cold, the flu can cause rapid deterioration, so early detection and proper care are essential.
Treatment Without Medicine
Mild cases of influenza can often be managed naturally without medication. Effective remedies include:
- Plenty of rest: Allows the body to focus energy on fighting the infection.
- Stay hydrated: Drink warm water, soups, and herbal teas to prevent dehydration.
- Steam inhalation: Helps relieve nasal congestion and promotes easier breathing.
- Saltwater gargle: Soothes a sore throat and reduces throat irritation.
- Warm compresses: Alleviate body aches and muscle soreness.
- Natural remedies: Ginger, honey, turmeric milk, and tulsi (holy basil) possess antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Nutritious diet: Foods rich in vitamins and minerals accelerate recovery.
⚠️Note: Severe flu cases, high fever, or individuals with chronic conditions should seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention of Influenza
Preventing influenza is far better than treating it. Key preventive measures include:
- Annual flu vaccination: Provides the best protection against seasonal flu.
- Hand hygiene: Wash hands regularly with soap and water.
- Avoid close contact: Steer clear of individuals showing flu symptoms.
- Wear masks: Especially in crowded places or during peak flu season.
- Healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep strengthen immunity.
Taking these steps not only protects you but also helps reduce the spread of influenza in your community.
Healthy Diet for Flu Recovery
Diet plays a crucial role in boosting immunity and supporting recovery from influenza. Include these nutrient-rich foods:
- Vitamin C-rich foods: Oranges, kiwi, guava, and bell peppers strengthen the immune system.
- Zinc-rich foods: Lentils, chickpeas, and pumpkin seeds promote faster healing.
- Probiotics: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods improve gut health and immunity.
- Warm soups & broths: Help maintain hydration and provide essential nutrients.
- Herbal teas: Tulsi, ginger, and lemon teas reduce inflammation and support respiratory health.
A balanced diet combined with adequate rest enhances the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Risk Factors for Severe Influenza
Certain groups are more susceptible to complications from influenza:
- Children under 5 years
- Adults over 65 years
- Pregnant women
- People with chronic illnesses such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease
- Immunocompromised individuals
- People with poor nutrition or weakened immunity
Identifying high-risk groups allows for proactive measures, including vaccination and prompt medical care.
Global Impact of Influenza
Influenza has far-reaching effects on public health and the global economy.
- Seasonal outbreaks: Occur annually and affect millions worldwide.
- Pandemics: Historical pandemics like the 1918 Spanish Flu and 2009 H1N1 caused millions of deaths.
- WHO statistics: Seasonal influenza leads to 3–5 million severe cases and up to 650,000 deaths every year.
- Economic impact: Flu-related absenteeism in schools and workplaces reduces productivity, while healthcare systems face increased burdens.
Understanding the global impact highlights the importance of vaccination, hygiene, and public health measures.
Conclusion
Influenza is more than a seasonal nuisance—it is a serious viral illness that demands attention and preventive action. Most cases are mild and recover naturally, but vulnerable groups can experience dangerous complications.
The best defense against influenza is a combination of vaccination, proper hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle. For those who contract the flu, rest, hydration, nutritious foods, and natural remedies can accelerate recovery.
Being aware, prepared, and proactive not only protects your health but also helps reduce the global burden of influenza.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is influenza?
Influenza, or flu, is a viral infection affecting the respiratory system that spreads easily from person to person.
2. What are the common symptoms?
High fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, headache, fatigue, and sometimes nausea or diarrhea.
3. How is influenza different from a common cold?
Flu symptoms are more severe, sudden, and prolonged, while colds are milder and gradual.
4. Can influenza be treated without medicine?
Yes, mild flu cases can be managed with rest, hydration, steam inhalation, herbal remedies, and nutritious foods. Severe cases require medical attention.
5. How can I prevent influenza?
Annual vaccination, regular handwashing, wearing masks, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and maintaining strong immunity.
6. Who is at high risk of complications?
Young children, older adults, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic illnesses or weakened immunity.
7. What is the global impact of influenza?
Influenza causes millions of infections and severe cases annually, hundreds of thousands of deaths, and significant economic and healthcare burdens.
🔑 SEO Elements
Meta Title: Influenza: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Global Impact
Meta Description: Learn about influenza (flu), its causes, symptoms, prevention, natural treatment, and global impact. Stay healthy with diet and lifestyle tips.
Slug: /influenza-causes-symptoms-treatment-prevention
Keywords: influenza, influenza symptoms, influenza causes, influenza prevention, influenza treatment without medicine, global impact of influenza, flu recovery diet