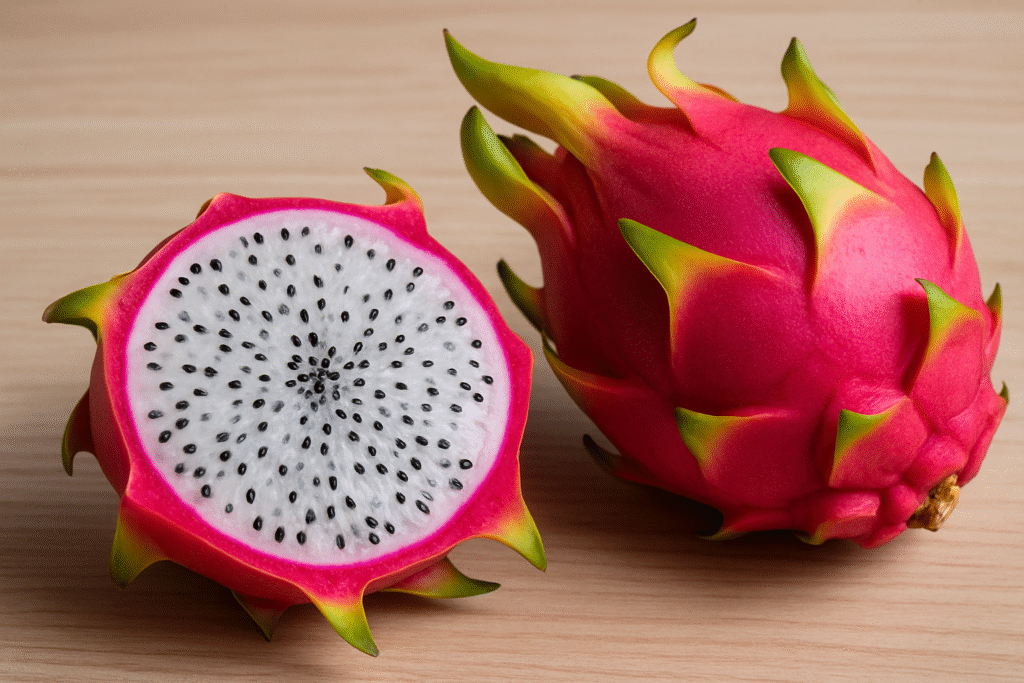
Dragon fruit, also called pitaya or pitahaya, is one of the most eye-catching fruits in the world. With its vibrant pink or yellow skin, flame-like scales, and speckled flesh, it has captured attention not only for its exotic looks but also for its nutritional and health benefits.
Behind its striking appearance lies a fruit rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber — making it a valuable addition to modern diets. From smoothie bowls to skincare research, dragon fruit is now found in kitchens, markets, and even laboratories worldwide.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about dragon fruit: its origins, varieties, nutrition, health benefits, how to enjoy it, sustainability, and FAQs.
Origins and Varieties of Dragon Fruit
Dragon fruit grows on climbing cacti of the Hylocereus and Selenicereus genera. Originally native to Central and South America, it is now cultivated widely in Southeast Asia, India, the Caribbean, and Australia.
Common Varieties of Pitaya
- White-fleshed pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) – Pink skin, white pulp, mildly sweet.
- Red-fleshed pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus) – Magenta flesh, higher in antioxidants.
- Yellow pitaya (Hylocereus megalanthus) – Yellow skin, white pulp, sweeter flavor.
Nutritional Value of Dragon Fruit
Dragon fruit is low in calories but packed with hydration, fiber, and antioxidants, making it a light yet nutrient-dense option.
Average Nutrition per 100g (USDA Data):
- Calories: 60–90 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 12–15 g
- Fiber: 3–4 g
- Vitamin C: 3–6 mg
- Magnesium: 10–20 mg
- Omega-3 and omega-6 fats: Found in the tiny black seeds
Key Note: Red and purple pitaya varieties are richer in betalains, natural pigments with powerful antioxidant activity.
Health Benefits of Dragon Fruit
Scientific studies suggest several potential health benefits of dragon fruit, though more research is needed.
1. Rich in Antioxidants
Dragon fruit contains vitamin C, flavonoids, and betalains, which help reduce oxidative stress and support immune health.
2. Supports Digestive Health
The fiber content promotes healthy digestion and may act as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria.
3. Heart and Metabolic Benefits
Emerging research shows dragon fruit may help:
- Balance cholesterol
- Regulate blood sugar
- Support weight management
4. Skin and Beauty Potential
Dragon fruit peel extracts are being studied for natural skincare, thanks to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
How to Select, Store, and Eat Dragon Fruit
- Choosing: Pick fruits with bright, even-colored skin and slight softness. Avoid wrinkled or mushy ones.
- Storage: Store whole fruit at room temperature for 2–3 days or refrigerate for up to 2 weeks. Eat cut fruit within 48 hours.
- Preparation: Slice in half and scoop out the flesh, or peel and cube. The skin is not edible.
Delicious Ways to Enjoy Dragon Fruit
Dragon fruit is versatile and can be enjoyed in many recipes:
- Smoothie Bowls – Blend pitaya with banana and coconut water, top with granola and seeds.
- Tropical Salads – Mix with mango, pineapple, and citrus dressing.
- Dragon Fruit Salsa – Combine with lime juice, cilantro, and chili for tacos or grilled fish.
- Infused Water – Add slices with cucumber and mint for a refreshing drink.
Sustainability and Innovation
Dragon fruit is not just healthy but also eco-friendly. The cactus thrives in semi-arid regions and requires less water than many other fruits.
Researchers are exploring innovative uses for dragon fruit peel and pulp in:
- Natural food colorants
- Health supplements
- Biodegradable products
This makes dragon fruit a model for sustainable agriculture.
Safety and Considerations
- Allergies: Rare, but possible. Test with small amounts if eating for the first time.
- Sugar Content: Contains natural sugars — people with diabetes should eat in moderation.
- Color Effects: Red-fleshed varieties may temporarily tint urine or stool pink/red. This is harmless.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What does dragon fruit taste like?
It has a mildly sweet flavor, similar to kiwi and pear, with a soft texture and crunchy seeds.
2. Is dragon fruit good for weight loss?
Yes. It’s low in calories, high in fiber, and hydrating, making it a filling yet light option.
3. Can people with diabetes eat dragon fruit?
Yes, in moderation. Its fiber helps regulate sugar absorption, but those with diabetes should consult their doctor before eating large amounts.
4. Is dragon fruit safe during pregnancy?
Generally, yes. It provides vitamin C, fiber, and hydration. Wash thoroughly before eating.
5. Can you eat dragon fruit skin?
No, the skin is not edible. Consume only the flesh.
6. Why does dragon fruit change urine or stool color?
Red varieties contain betalain pigments, which may temporarily tint urine or stool. It’s harmless.
7. How do I know if dragon fruit is ripe?
Ripe fruit has bright, even skin color and yields slightly when pressed. Overripe fruit feels mushy.
8. Does dragon fruit improve skin health?
Yes. Its antioxidants and vitamin C support skin health. Extracts are being researched for skincare use.
Final Thoughts
Dragon fruit is not only a feast for the eyes but also a nutrient-packed superfruit. With its blend of fiber, antioxidants, vitamin C, and hydration, it makes a perfect addition to health-conscious diets.
Whether you enjoy it fresh, in smoothies, salads, or unique recipes, dragon fruit brings both beauty and benefits in every bite — making it one of the world’s most extraordinary fruits.
Sources – USDA FoodData Central – Dragon Fruit Nutrition Data